🔷Remove Pallet Point Cloud
Function Description
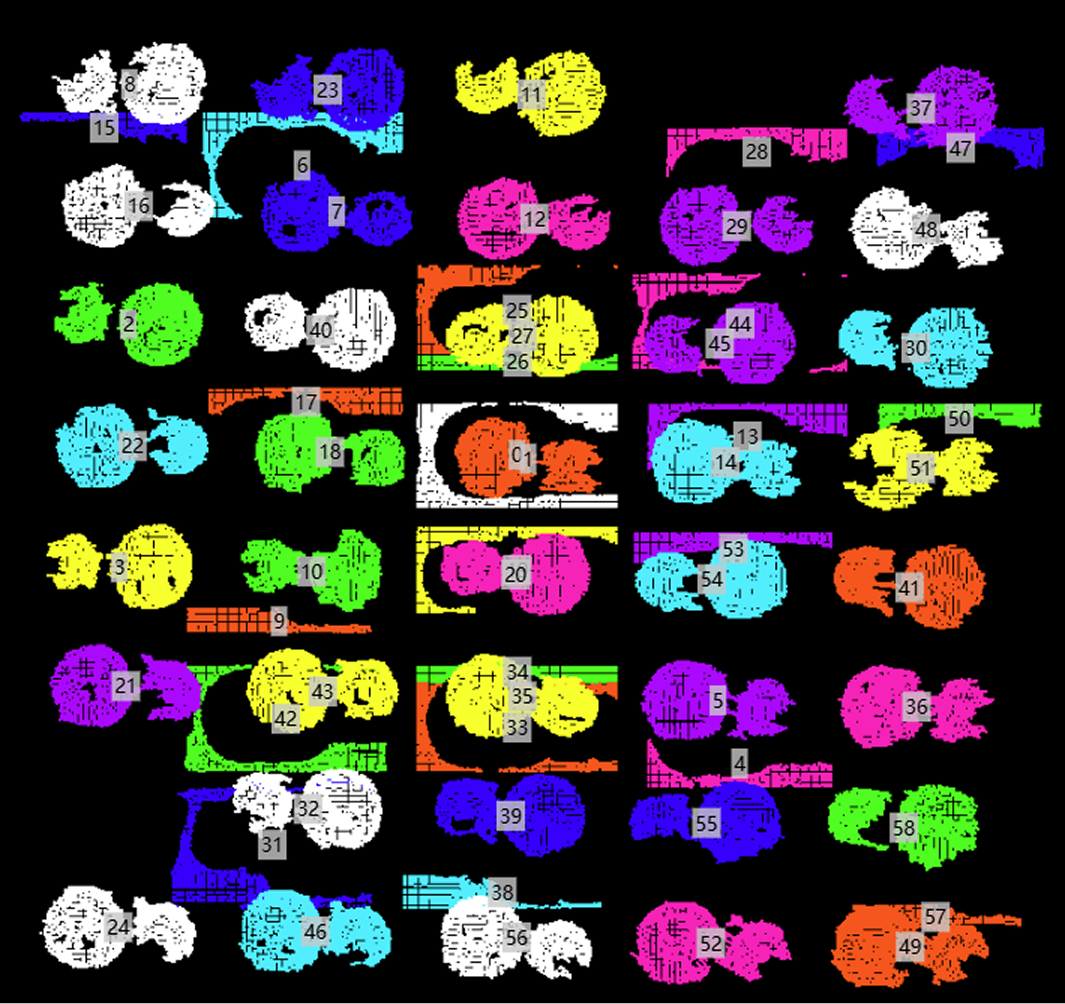
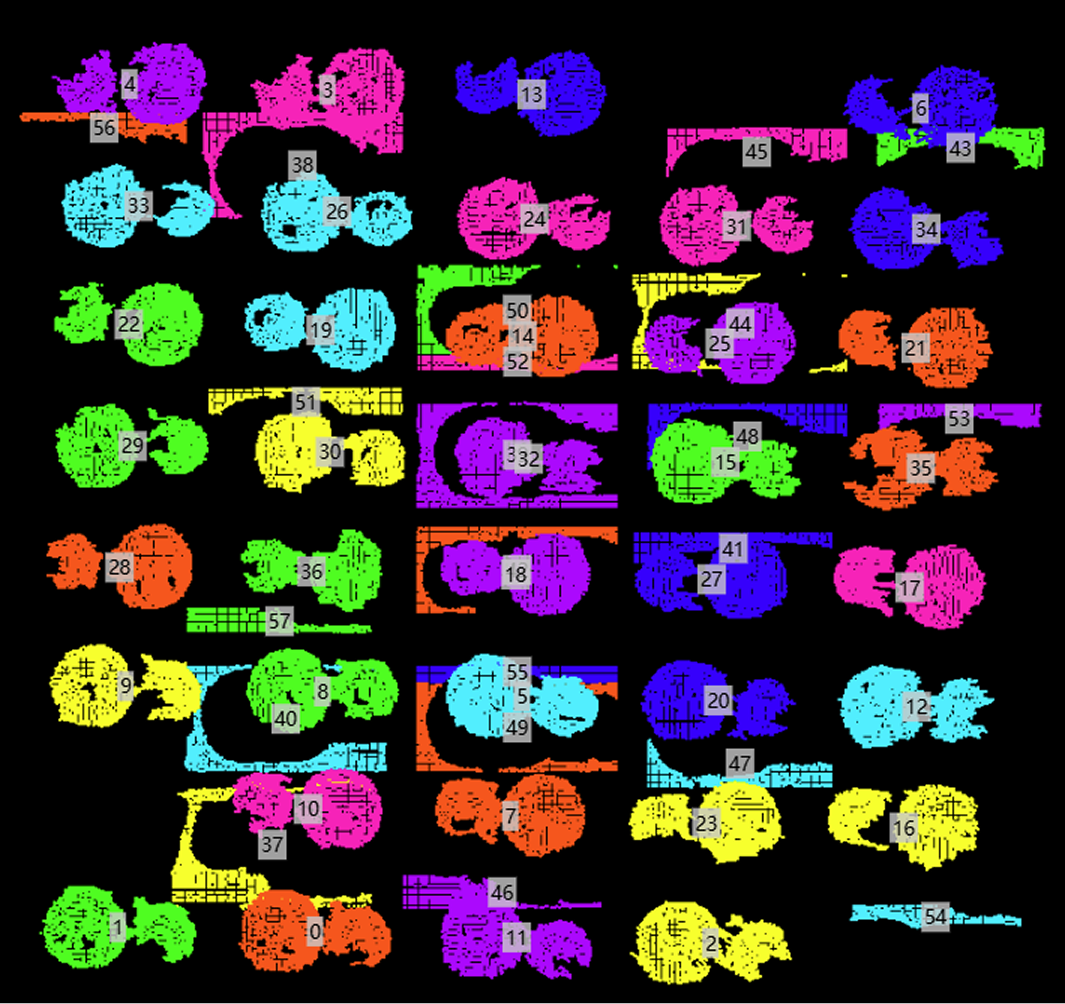
This operator is designed to process point cloud data placed on pallets. It can receive a list containing multiple point clouds, attempt to identify the point cloud representing the pallet, and separate it from point clouds representing objects. The operator determines which point cloud is the pallet by analyzing the quantity and spatial position (especially height) of point clouds, and it calculates and outputs an ROI surrounding the object point clouds.
Usage Scenarios
-
Robot Depalletizing/Palletizing : In automated depalletizing or palletizing applications, it’s necessary to separate pallets from goods on the pallets to process goods individually or locate the pallet itself.
-
Point Cloud Preprocessing : As part of the point cloud processing pipeline, remove supporting structures (such as pallets, tabletops) from the scene, keeping only point clouds of objects of interest.
Input Output
Input |
Clustered Point Cloud: A list containing one or more point clouds (usually representing object clusters and pallets). |
|
Output |
Pallet Point Cloud: Point cloud identified as pallet (may be None). |
|
Removed Point Cloud: Point cloud list remaining after removing pallet point cloud from input list. |
|
|
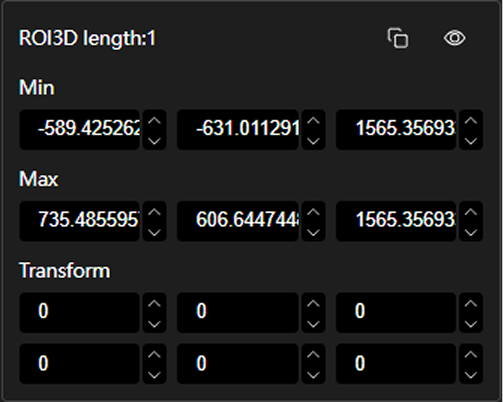
Point Cloud ROI: ROI three-dimensional bounding box containing the pallet point cloud. |
|
Parameter Description
|
This operator has two versions:
Both have identical core functionality and parameters, differing only in the type of point cloud data processed. |
|
Input Requirements : The operator expects input to be a point cloud list, usually clustered results, where one element represents the pallet and other elements represent cargo clusters. The input point cloud count must be greater than 1. |
Layer Height
Parameter Description |
Height threshold used to distinguish between pallet and cargo layers. The operator calculates the Z coordinate of point cloud cluster centers. If the difference between a point cloud cluster’s center Z coordinate and that of the cluster with the most points (usually considered object point cloud) exceeds this layer height, the cluster is considered to possibly belong to a different layer (possibly pallet). |
Parameter Adjustment |
Set according to the actual height difference between pallet and cargo layers. If the height difference between pallet and bottom cargo layer is significantly greater than 100mm, the default value may be applicable. If the layer height is small or the pallet is thin, this value should be appropriately reduced. If cargo layers themselves have large height differences, this value may need to be increased to avoid mistakenly identifying cargo layers as pallets. |
Parameter Range |
[1,10000], Default: 100, Unit: mm |
Center Calculation Method
Parameter Description |
Select the method for calculating the center point Z coordinate of each point cloud cluster, which is used to determine layer height differences. |
Parameter Adjustment |
|
Z-Axis Orientation
Parameter Description |
Defines the expected direction of the pallet relative to the top of the stack (highest point of cargo) in the scene. |
Parameter Adjustment |
|
X/Y/Z Axis Negative/Positive Extension Values
Parameter Description |
Define the extension amount of the output ROI (three-dimensional bounding box) relative to the center and range of the detected pallet area. Negative extension values are usually negative numbers, indicating extension toward the negative direction of coordinate axes; positive extension values are usually positive numbers, indicating extension toward the positive direction of coordinate axes. |
Parameter Adjustment |
These parameters are used to adjust the size of the output ROI. Default values will extend or contract specified distances in positive and negative directions of each axis based on the calculated pallet center and overall point cloud XY range. |
Parameter Range |
All ranges are [-1000,1000], Unit: mm. |
Enable Node
Parameter Description |
Controls whether this operator performs pallet removal and ROI calculation operations. |
Parameter Adjustment |
|