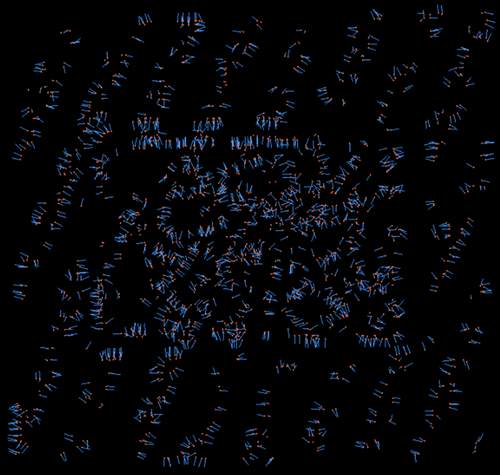🔷Point Cloud Edge Extraction - Unordered (Legacy)
Functional Description
This operator is used to extract edge points from input unordered point clouds with normals. It identifies edges by analyzing normal vector direction differences between each point in the point cloud and its neighboring points, with options to use K-nearest neighbor (KNN) or radius search (RADIUS) to define neighborhoods. If the maximum angle difference between a point and points in its neighborhood exceeds the set "Edge Angle Threshold", that point is identified as an edge point. The operator can also choose whether to adjust output edge points' normal vector directions.
Usage Scenarios
-
Suitable for scenarios requiring compatibility with legacy workflows.
-
Feature Extraction: Extract contours or geometric edges of unordered point clouds.
-
Visualization: Highlight object contours
Input Output
Input |
Point Cloud with Normals: Input must be unordered point clouds or point cloud lists containing normal vector information. |
|
Output |
Point Cloud Edges: Point cloud list composed of extracted edge points. Output point cloud contains only points identified as edges and preserves their original coordinate and normal vector information (normals may be adjusted). |
|
Parameter Description
Edge Angle Threshold
Parameter Description |
Normal vector angle difference threshold for determining whether a point is an edge point. |
Parameter Adjustment |
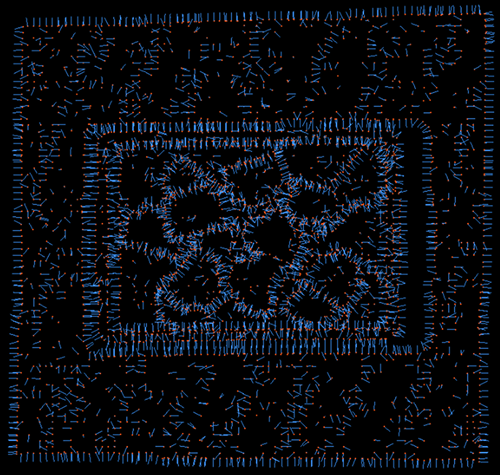
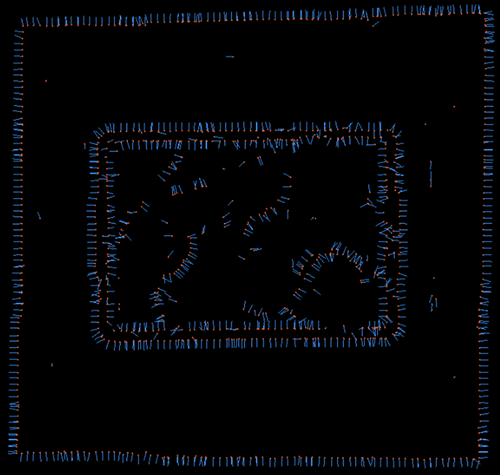
The operator calculates angle differences between each point and its neighboring points' normal vectors. If the maximum value among these angle differences exceeds the threshold set here, that point is considered an edge point.
|
Parameter Range |
[0, 180], Default value: 90, Unit: degrees |
|
|
|
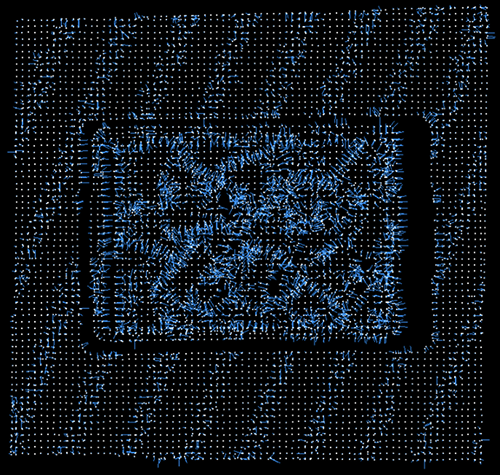
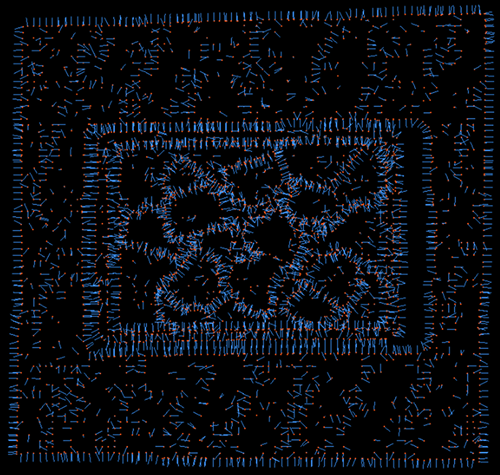
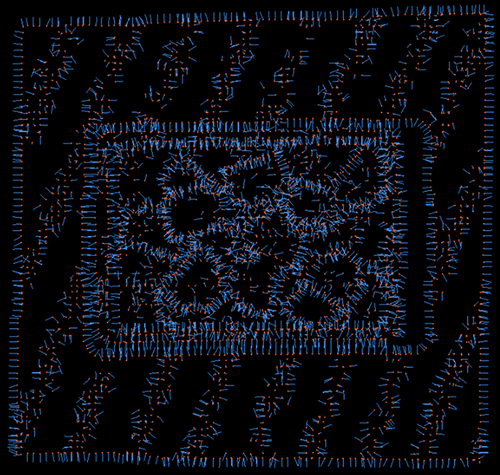
Edge Angle Threshold=10 |
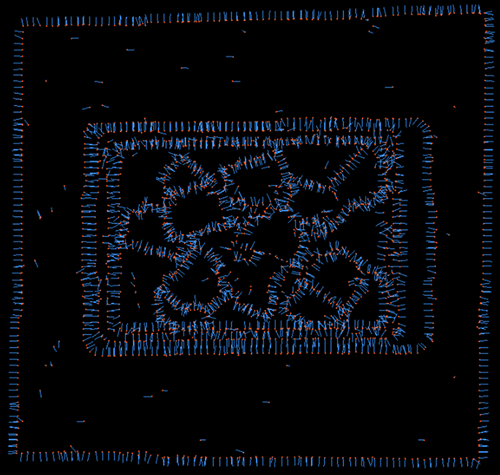
Edge Angle Threshold=90 |
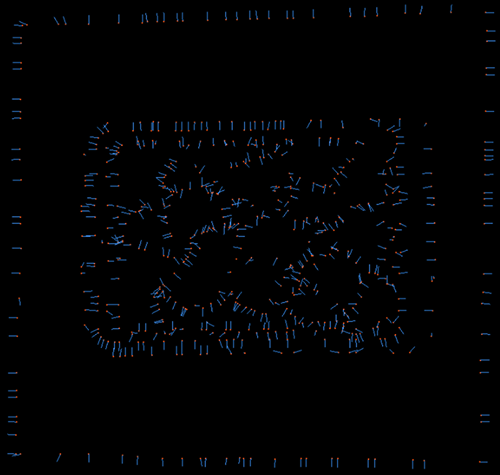
Edge Angle Threshold=180 |
Adjust Edge Normals
Parameter Description |
Choose whether to adjust normal vectors after extracting edge points. |
|
Parameter Adjustment |
On (Default): Recalculate and adjust normal vectors of identified edge points to make them as perpendicular as possible to edge direction and point in consistent direction (outward or inward). |
|
Off: Preserve original normal vectors of edge points. |
|
|
Neighbor Search Method
Parameter Description |
Choose method for defining neighborhood range of each point. |
|
Parameter Adjustment |
Count Search (Default): Find the nearest K points to current point as neighborhood, meaning always take fixed number of neighboring points regardless of actual distances between these points. K value is specified by "Neighbor Search Count" parameter. |
|
Radius Search: Search with fixed physical distance as radius, find all points within this range. Radius value is specified by "Neighbor Search Radius" parameter. |
|
|
Neighbor Search Count
Parameter Description |
Effective when "Neighbor Search Method" selects "Count Search". |
Parameter Adjustment |
Controls number of neighboring points:
|
Parameter Range |
[0, 100000], Default value: 20 |
|
|
|
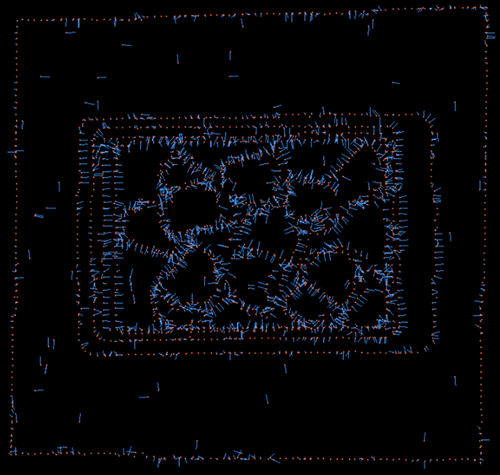
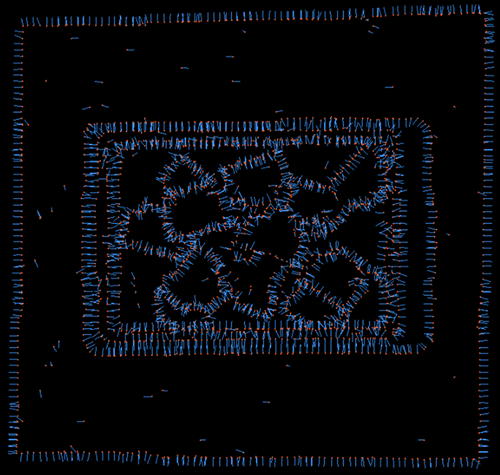
Neighbor Search Count=10 |
Neighbor Search Count=20 |
Neighbor Search Count=100 |
Neighbor Search Radius
Parameter Description |
Effective when "Neighbor Search Method" selects "Radius Search". |
Parameter Adjustment |
Controls spatial range of neighborhood for angle difference calculation:
|
Parameter Range |
[0, 1000], Default value: 10 |
|
|
|
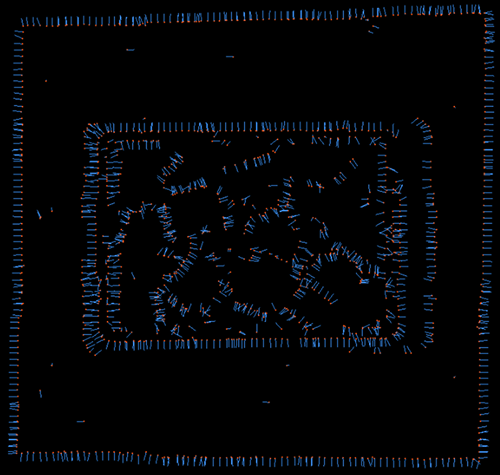
Neighbor Search Radius=5 |
Neighbor Search Radius=10 |
Neighbor Search Radius=50 |