🔷Point Cloud Normal Estimation
Functional Description
This operator is used to estimate surface normal vectors for each point in input point cloud data.
A normal vector is a three-dimensional vector perpendicular to the local surface where a point is located, representing the orientation of that point.
The operator uses a K-nearest neighbor based method: for each point in the point cloud, it finds its nearest K neighboring points, then fits a local plane through these neighboring points. The normal vector of this plane serves as the normal vector estimate for that point.
Usage Scenarios
-
Feature Extraction: Normal vectors and their distribution are important geometric features that can be used for point cloud matching, segmentation, and recognition tasks.
-
Plane Fitting and Detection: Normal vector information helps identify and segment planar regions.
-
Surface Analysis: Analyze object surface curvature, smoothness, etc.
-
Robot Grasping: When determining object surface graspability or calculating grasping poses, normal vector information may be needed.
Input Output
Input |
Point Cloud: Input point cloud or point cloud list containing only XYZ coordinate information. |
|
Output |
Point Cloud with Normals: Output point cloud or point cloud list that includes original XYZ coordinates plus estimated normal vector information for each point. |
|
Parameter Description
|
Viewpoint
Parameter Description |
Defines a three-dimensional coordinate [X, Y, Z], usually camera coordinate system origin [0, 0, 0], used to adjust computed normal vector directions. |
Parameter Adjustment |
Normal vectors have two possible directions (pointing inward or outward from surface). After computing initial normal vectors, the operator calculates the angle between the vector from current point to viewpoint and the initial normal vector. If the angle is greater than 90 degrees, the operator reverses the normal vector to ensure normal vectors roughly point toward the viewpoint direction. |
Parameter Range |
Default value: [0,0,0] |
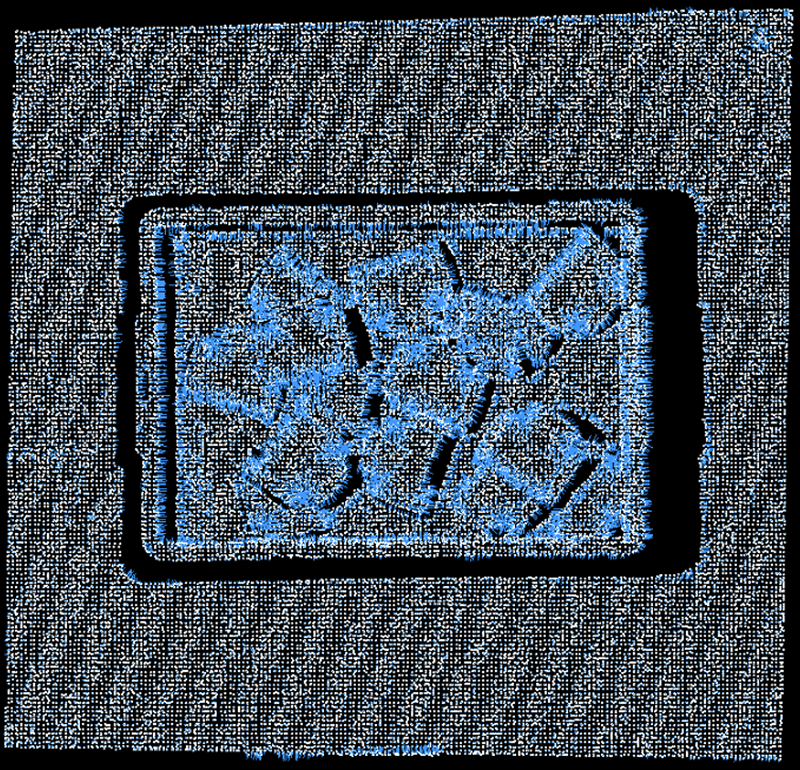
Search Count
Parameter Description |
Number of neighboring points to find around each point when estimating normal vectors. These neighbors are used to fit a small plane, and the plane’s normal vector becomes that point’s normal vector. |
Parameter Adjustment |
Search count selection affects normal vector estimation stability and sensitivity to local details.
Need to select appropriate search count based on point cloud density, noise level, and application requirements. |
Parameter Range |
[1, 200], Default value: 15 |
|
|
|
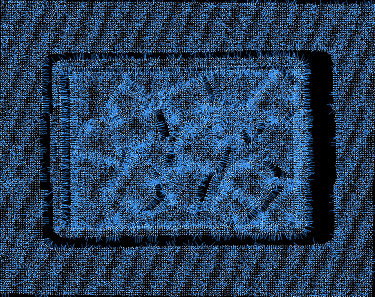
Search Count=5 (Detail Sensitive) |
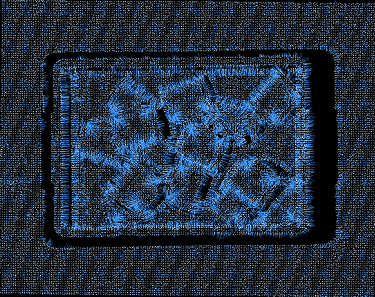
Search Count=15 (Default) |
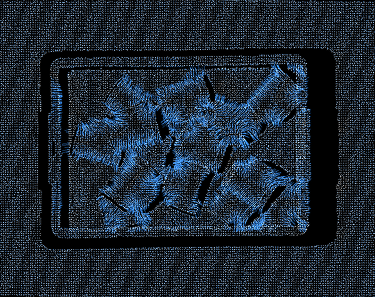
Search Count=200 (Highly Smooth) |