Matching template editing tool
Introduction
The Matching template editing tool is used to edit matching templates, such as cropping point clouds, downsampling point clouds, adding pick points, etc.
The matching template files created by the Matching template editing tool are used in the 3D coarse matching, 3D coarse matching v2, 3D fine matching, and 3D fine matching (Undirected) operators in ATOM.
Interface introduction
The Matching template editing tool mainly consists of the following four parts:
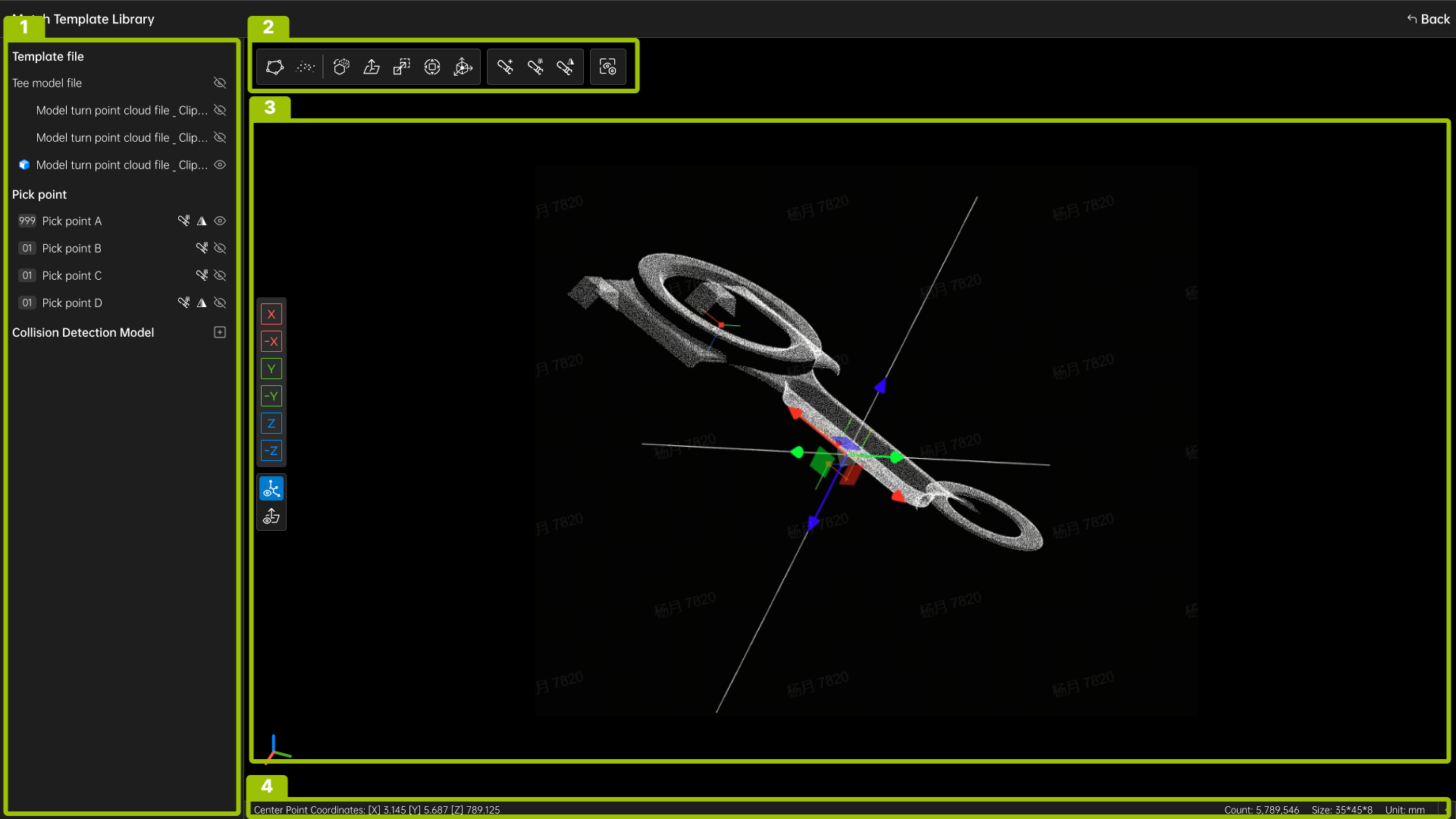
Area |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
1 |
File Management |
This area displays template files, pick point files, and collision model files. |
2 |
Toolbar |
|
3 |
3D editing area |
This area is used for model editing and displays the coordinate axis and normal of the pick points. |
4 |
Bottom Information Bar |
This area displays the centerline point coordinates, point cloud coordinates, point count, dimensions, and unit information. |
Application guide
A good template point cloud should be as noise-free as possible, with even distribution of points and sufficient features. Depending on the actual situation, you can use a face template or an edge template. The selection and processing of the template point cloud directly affects the effect of 3D matching, and should be reasonably selected and processed according to specific application requirements and object features.
-
The surface template is mainly composed of points on the surface of the object and contains a large amount of surface geometric information. It is suitable for objects with significant surface features.
-
The edge template is composed of the edge points of the object, and mainly focuses on the object contour and edge features.
Surface template
The main production process of the surface template is as follows:
-
Cut point cloud (optional): Cut out the point cloud outside the matching part and only keep the matching part.
-
Point cloud downsampling (optional): Downsample the point cloud to improve the matching speed while taking into account the matching accuracy.
-
Add pick point: Directly add a pick point or teach a pick point.
Edge template
The main production process of edge template is as follows:
-
Cut point cloud (optional): Cut out the point cloud outside the matching part and keep only the matching part.
-
Point cloud downsampling (optional): Downsample the point cloud to improve the matching speed while taking into account the matching accuracy.
-
Add pick point: Add pick point directly or teach pick point.